Loops in c
Repetition of a set of instructions in a program is called loops in c.
Loops in c involve repeating some portion of the program either a specified number of times or until a particular condition is being satisfied.
Looping increases the versatility of the program.
There are three loops in c that can be used to repeat some portion of a program.
1. while loop
2. for loop
3. do-while loop
Let us discuss each loop one by one
while loop
There is some portion in a program that we want to repeat a fixed number of times in such cases we can use a while loop.
Let us take an example,
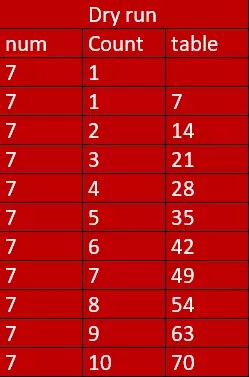
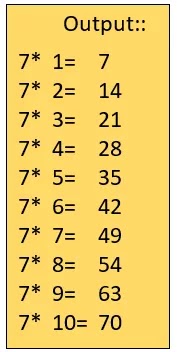
Query- print the table of 7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int num=7; int count=1,table; while(count<=10) { table=num*count; printf(“%d*%d=d”,num,count,table); count++; } getch(); } |
Flow chart:
- The program is, printing the table of 7.
- Now to print the table of seven, we need logic or algorithm that will process 10 times.
- For this, here we need a loop, and a condition where a loop will process 10 times, i.e., 10 times the logic should process.
- The second thing we need a counter that should be set to 1 and gets incremented until the condition applied is valid.
- We have used while loop and under ( ) braces of while loop we have applied the condition, “counter <=10”.
- Then we have applied the logic for the table.
- After the first process, we have incremented the counter and, the counter gets incremented and, logic gets processed till the counter is 10.
- When the counter becomes 11, the condition gets false and, the loop gets over.
Important points to remember
1. Instead of count++ we can also write count=count+1 or count+=1.
You must be knowing that (++) is increment operator and (--) is decrement operation.
Increment operator (++) = increment operator is used to increment the loop counter.
The decrement operator (--) = decrement operator is used to
decrementing the loop counter.
2. By using (++) or (--) operator, we can only increment or
decrement by 1.
Using count=count+1 format, we can increment or decrement by other than 1.
eg. count=count+2, count=count +3 these is increment.
count = count-2, count= count -3 these is decrement.
Note that here count is just an integer variable that we have used as a loop counter. We can use any other variable name as per our choice.3. It is not necessary that the loop counter should be int we can also use a float loop counter.
#include<stdio.h> int main() { float i=0.1; while(i<=0.10) { printf(“hello world”); i=i+0.1; } return 0; }
We can also decrement the floating loop.
4. While(i<=10);
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int i=1; while(i<=10); { printf(“hello world”); i++; } return 0; }
· As you can see in the above program, after the while statement there is a semicolon (;).
· while(i<=10); here is a semicolon after the while statement, the semicolon is a sign of termination, which means when we give termination symbol (;) after the while statement, the while loop gets terminated till (;). i.e., the statements present in the curly braces{} which are the body of a while loop will not be considered as the body of a while loop. The statements under curly braces will not be part of the while loop.
#include<stdio.h. int main() { int i=0; while(i++<=10) { printf(“%d\n”,i); } return 0; }
· In the program above, the condition and loop counter incrementation is done under a single while( ) round braces. We have not used a separate line for the loop counter.
· In the line while(i++<=10) value of subscript "i" is first compared with the condition after that it is incremented.
· i++ is called as post increment.
· After checking the condition, the value "i" increments and, perform the operation under while loop body under the { } curly braces.
· That is why subscript "i" should be initialized to 0, not 1.
5. Pre-increment#include<stdio.h> int main() { int i=0; while(++i<=10) { printf("%d\n",i); } return 0; }
· The only difference between the previous program and this program is ++i.
· Here first the value of subscript "i" is incremented then it is compared with the condition. Hence incrementation of "i" becomes before the comparison.
· ++i is called as pre-increment.
To know more about increment and decrement operator follow the below link,
increment and decrement operator in c
See Also:
for loopdo-while loop
break statement
continue statement

Post a Comment
Post a Comment